14 March 2021
Resource Center
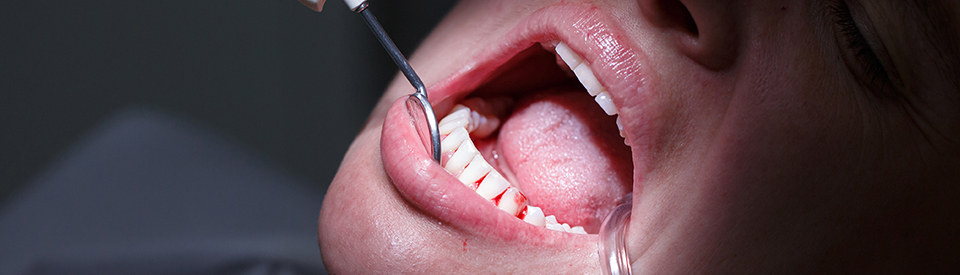
Periodontal disease is a gum infection that can cause serious damage to the soft tissues in your mouth. Also known as gum disease, periodontal disease can cause your teeth to loosen and shift. If left untreated, periodontal disease can spread to the bone that supports your teeth and can even cause tooth loss.
Periodontal disease is one of the most common oral health issues in the United States. However, it is completely preventable with attention to oral hygiene, including regular brushing and flossing, as well as routine dental visits to remove plaque buildup. While these preventive measures are key, it is important to recognize signs of periodontal disease to reduce your chances of letting the condition advance and cause tooth or bone loss.
Symptoms of Periodontal Disease
Your gum tissue should appear firm and pink, forming very closely to your teeth. If you notice these symptoms of unhealthy gum tissue, schedule an appointment with your dentist:
- Discolored gums. Instead of pale pink, unhealthy gums affected by periodontal disease may appear bright red, dark red, or even purple. In general, any color change in your gums may signify an issue.
- Swollen or enlarged gums. Gums should be firm but not puffy or distended looking. Swollen gums are a sign of inflammation, which is a key symptom of periodontal disease.
- Bad breath. Halitosis, or chronic bad breath, is a key indicator of a bacterial infection of the mouth's soft tissues. If you notice bad breath even after brushing, periodontitis may be to blame.
- Painful gums. Gums should not be tender to the touch or hurt after brushing and flossing. If you notice pain not associated with a cavity or injury, you may be dealing with periodontitis.
- Bleeding gums. While a pink-tinged toothbrush can be the result of over-vigorous brushing, healthy gums should not bleed easily after routine brushing and flossing. If you notice blood on your toothbrush or are spitting out blood after brushing, your gum tissue is likely unhealthy.
- Receding gums. Normal gum tissue sits tightly against the base of the tooth. If you notice your gums pulling away from your teeth, making your teeth appear longer, periodontitis could be to blame.
- Loosening or shifting teeth. Over time, as periodontal disease begins to affect the bone located beneath the gums, teeth are able to loosen, shift, or fall out. These changes can affect the way your teeth fit together and cause gaps, overlaps, painful chewing, or other bite issues.
Experiencing the above symptoms of periodontitis necessitates a trip to the dentist. However, if you are unable to schedule an appointment with your regular dentist, consider searching for a dentist in your area that accepts patients on an emergency basis. Contact Emergency Dental Service at 1-888-350-1340 or reach out online to request a list of dental providers near you.